-
Kollmorgen AKT2G-AC-FAN-001 fan cartridge
-
Kollmorgen AKT-AN-820-000 8-Channel Analog Input Terminal
-
Kollmorgen 4-Channel Analog Input Terminal (AKT-AN-420-000)
-
METSO D201379 PC Board PLC & ADD-ON Board
-
Metso PDP403 Distributed Processing Unit
-
Alfa Laval EPC 60 Retrofit kit
-
ABB Digital annunciator unit SACO 64D4
-
ABB Model 264DD Differential/Gauge
-
ABB Alarm annunciators
-
ABB SACO 16 A3 Analog Annunciator Unit
-
Kollmorgen AKD PDMM® Programmable Drive, Multi-Axis Master
-
Kollmorgen PCMM: Programmable Controller, Multi-Axis Master
-
Kollmorgen PCMM2G: Next-Generation Performance in a Powerful, Compact Controller
-
Kollmorgen P80630 Stepper Drive
-
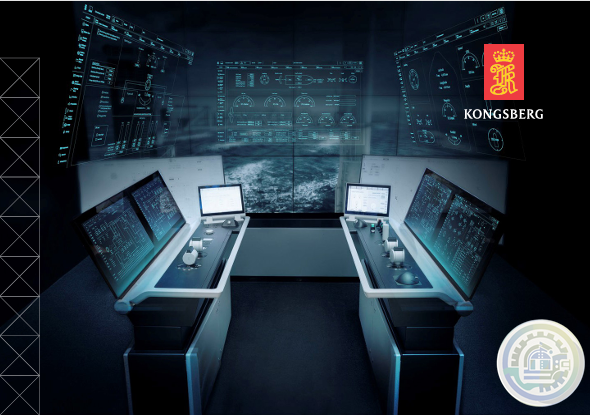
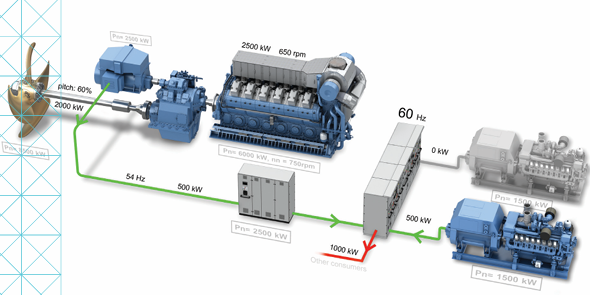
Kongsberg Maritime System and vessel conversions
-
ADLINK CPCI-3840 3U CompactPCI Intel® Pentium® M Processor Module
-
ABB Digital Annunciator Unit SACO 16D1
-
ABB SACO16D1-AA Digital Annunciator Unit
-
Kongsberg HIPAP® 352P PORTABLE HIGH PRESICION ACOUSTIC POSITIONING
-
Kongsberg MRU 5 Motion Reference Unit
-
Kongsberg MRU 5+ Motion Reference Unit
-
Kongsberg KONGSBERG MARITIME PROPULSION SYSTEMS Active Front End (AFE)
-
Kongsberg HiPAP 352P Portable acoustic positioning system
-
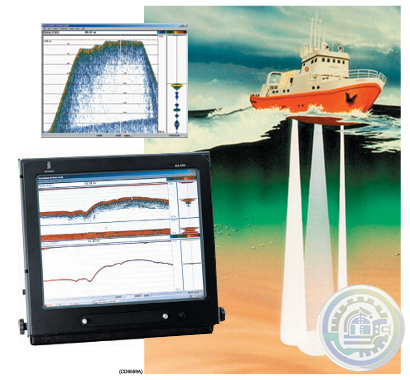
Kongsberg EA600 New generation precision hydrographic echo sounder
-
Kongsberg Digital Governor Unit (DGU) AutoChief® 600
-
Kongsberg AutoChief® 600 Propulsion Control System
-
Kongsberg K-Chief Vessel Automation System
-
Kongsberg AIS BS600 Automatic Identification System - Base Station
-
Kongsberg K-Chief 600 Alarm and Command Panel
-
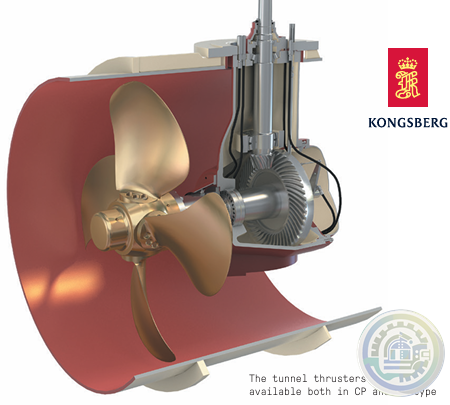
Kongsberg Tunnel Thrusters Type TT FP
-
Kongsberg AutoChief®600 Lever Telegraph Unit (LTU11)
-
YOKOGAWA Model AW810D Wide Area Communication Router
-
Watlow Eurotherm® 3200 Temperature/Process Controller
-
Watlow EtherCAT®, Fiber Optic Temperature Measurement and Control System
-
Watlow EZ-ZONE® RM Modular Controller Family
-
Watlow EFit SCR Power Controller
-
Watlow Basic Temperature and Limit Controllers
-
Watlow’s New WATCONNECT® Control Panels
-
Watlow EPack-2PH Compact SCR Power Controllers
-
Watlow Large and Extra-Large WATCONNECT® Panels
-
Watlow Eurotherm® EPack™ compact SCR power controllers-1PH -2PH -3PH
-
Watlow Eurotherm® EPack™ Lite Compact SCR Power Controllers
-
Watlow EPack™ Lite-1PH Compact SCR Power Controllers
-
Watlow’s new SERIES LS offers fixed limit set point temperature values
-
Watlow The SERIES LV limit family
-
Watlow’s family of microprocessor- based limit controllers SERIES LF
-
Watlow The EZ-ZONE RM controller simplifies thermal system management
-
Watlow The PM LEGACY™ series panel mount controller
-
Watlow EZ-ZONE® Remote User Interface (RUI)
-
Watlow Silver Series EM Operator Interface Terminal
-
The EZ-ZONE® ST integrated solid state controller from Watlow®
-
YOKOGAWA Cooling Water Pump Failure Prediction Monitoring
-
YOKOGAWA EJA Series Differential Pressure and Pressure Transmitters
-
YOKOGAWA EJA110E Diff erential Pressure Transmitter
-
YOKOGAWA AXF Magnetic Flowmeter Series
-
YOKOGAWA Turbomachinery Controller Overview (FCN-500/FCN-RTU)
-
YOKOGAWA STARDOM FCN-RTU Autonomous Controller
-
YOKOGAWA FCN Autonomous Controller Hardware (FCN-100)
-
YOKOGAWA STARDOM FCN-500 Autonomous Controller
-
CTI 2500-R4 Four-Slot Base with High-Speed Channel
-
CTI 2500P-J750 Janus PAC with 3MB Project Memory
-
CTI 2500C-J750“Janus”Compact Programmable Automation Controller
-
CTI 2500 Series® Compact Programmable Controllers
-
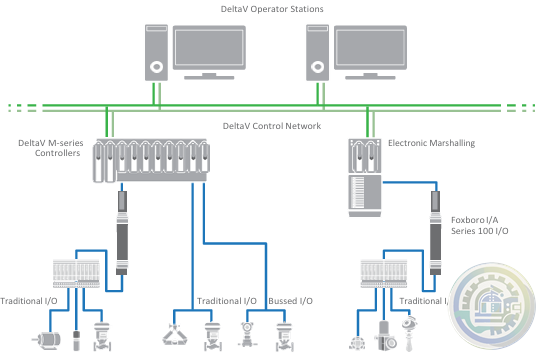
Emerson DeltaV™ Flex.Connect Solutions for Foxboro™ I/A Series 100 I/O
-
Emerson Modernization of Foxboro I/A Series® Systems to the DeltaV™ System
-
Foxboro DCS Fieldbus Modules for APACS+™ Automation Systems
-
Foxboro Evo™ Process Automation System
-
Foxboro™ DCS G61 Tricon Termination Enclosure
-
Foxboro G60 Tricon System Enclosure I/A Series® HARDWARE
-
Foxboro G62 and G72 Tricon System and Termination Enclosures
-
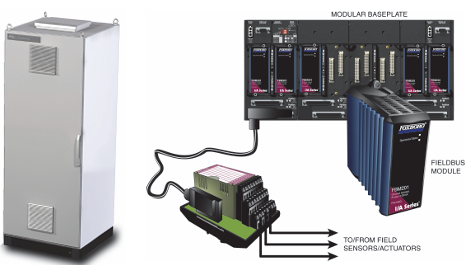
Foxboro I/A Series® Hardware DIN Rail Mounted Fieldbus Module Baseplate
-
Kongsberg K-Chief 600 Marine automation system
-
Kongsberg WCC 600 Watch Call Panels
-
Kongsberg Distributed Processing Units Remote Digital Output (RDo-16xe)
-
Woodward EM‐80 and EM‐300 Actuators All‐Electric Actuator System
-
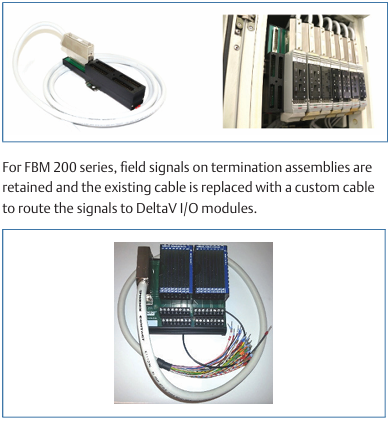
Foxboro DCS FBM for Migration of Bailey® Systems
-
Foxboro Migration with FCP280 and DCS FBMs
-
Foxboro DCS Fieldbus Modules for Siemens APACS+™ Automation Systems
-
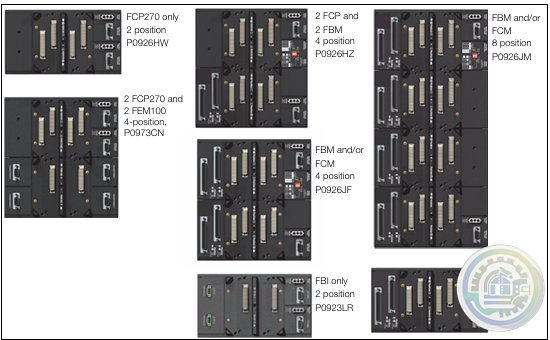
Foxboro 200 Series Baseplate Module Mounting
-
Foxboro Standard 200 Series Subsystem Overview
-
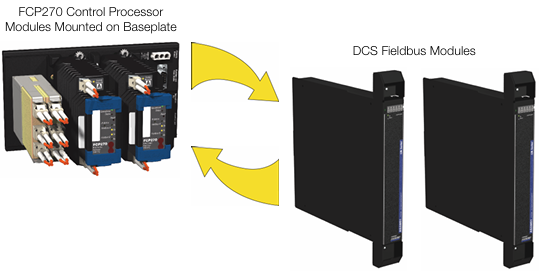
Foxboro Field Control Processor 270 (FCP270)
-
Johnson Controls DIS1710 Local Controller Display Installation Instructions
-
Johnson Controls FX-DIS Local Controller Display
-
Johnson Controls WRZ Series Wireless Room Sensors
-
Woodward EM-80/EM-300 Actuator System
-
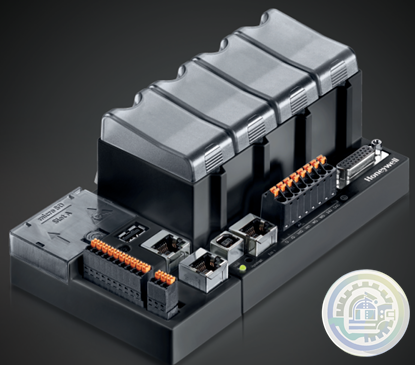
Honeywell ControlEdge™ PLC Modular Controllers
-
Honeywell CONTROLEDGE PCD Compact, Cyber Secure Control System
-
Honeywell M6410A, M7410F Non-Spring Return Cartridge Globe Valve Actuator
-
Honeywell ControlEdge™ HC900 How Does It Work?
-
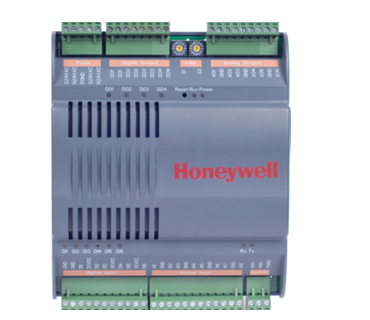
Honeywell ControlEdge HC900 controller
-
Honeywell HC900 Functional Overview
-
Honeywell Optimizer Advanced Controllers are a family of next generation integration & plant controllers
-
Honeywell Optimizer Advanced Controller
-
Honeywell Excel Web II Control System
-
Honeywell CPO-PLANT Controller area of the site
-
Honeywell ComfortPoint Niagara T1L VAV Controller
-
Honeywell ComfortPoint™ Open Plant Controller
-
Honeywell ComfortPoint Open CP-EXPIO (EXPANSION IO BOARD)
-
Honeywell ComfortPoint Open CPO-VAV2A-US (UNITARY CONTROLLER)
-
Honeywell ComfortPoint™ Open CPO-PC400 Plant Controller
-
Honeywell I/O MODULES EXPANSION MODULES & WIRING ADAPTER
-
Honeywell CPO-DIO ComfortPoint Open (DIGITAL I/O CONTROLLER)
-
Honeywell CP-Core ComfortPoint Open
-
Honeywell CPO-IO830A ComfortPoint Open MIXED I/O MODULE
-
Honeywell Sensepoint XCD
- Baldor
- Glassman
- Johnson Controls
- Studer
- Watlow
- AEG
- ADVANCED
- KEBA
- Bristol Babcock
- Rolls-Royce
- Aerotech
- APPLIED MATERIALS
- Basler
- SAACKE
- BENDER
- Kollmorgen
- MEGGITT
- METSO
- MITSUBISHI
- MTL
- HIMA
- Siemens
- BACHMANN
- AMAT
- DEIF
- DELTATAU
- EATON
- ELAU
- LAM
- SCHNEIDER
- Advantest
- ABB
- GE
- Emerson
- Motorola
- A-B
- KUKA
- Abaco
- HITACHI
- SST
- Vibro-Meter
- Rexroth
- Prosoft
- DFI
- Scanlab
- Reliance
- Parker
- Woodward
- MOOG
- NI
- FOXBORO
- Triconex
- Bently
- ALSTOM
- YOKOGAWA
- B&R
- UNIOP
- KONGSBERG
- Honeywell
- Omron
- CTI
- EPRO
- Tell:+86-18144100983
- email:kongjiangauto@163.com
- Application:wind/ petroleum/ chemical/ natural gas/ Marine/ mining/ aviation/ electronics/ steel/ nuclear power/ electric power/ coking/ air separation and so on
- Series:PLC/ DCS/ servo/ analog/ Ethernet/ digital/ redundant module/ tension system/ excitation/ generator management/ human-machine interface/ detection card/ sensor/ AC drive/ etc
Module Overview
Chapter Objectives
Stepper Controller
The Module overview will permit you to understand the basic functions of the Module and hardware requirements.
The Module, catalog number 1746–HSTP1, is an SLC 500 family compatible device. It can be used with any SLC 500 Processor.
The Module is configured through the SLC 500 backplane and requires no switch settings.
Motion can be programmed in either direction for over ±8,000,000 counts of absolute position.
An optional incremental encoder may be used to verify the position reached by the axis.


The Module does not automatically close a position loop in engineering units.
The feedback hardware can accept frequencies of up to 250 kHz for use as either loop back diagnostics or differential incremental encoder feedback devices.
The Module can be programmed for either incremental or absolute moves, depending on the application.
The Module supports two differential outputs, to suit the type of Stepper Translator used, which provide the following control commands:
• CW or non-directional pulse output
• CCW or direction signal output
Discrete inputs are provided for:
• External Interrupt
• Home Limit Switch
• Home Proximity Input
• CW Travel Limit Switch Input
• CCW Travel Limit Switch Input
• Pulse Train Enable/Disable Input
Differential inputs are provided for:
• Encoder Channel A and A NOT
• Encoder Channel B and B NOT
• Encoder Marker Channel

Command Mode Operation All stepper motor operations are performed in command mode.
This mode is entered by setting the mode flag (bit 15 in output word 0) to 0.
In command mode, the SLC Processor can issue commands and activate different operations or moves. The actions you can command are:
• Absolute Moves
• Relative Moves
• Hold Moves
• Resume Moves
• Immediate Stop Operations
• Homing Operations
• Jogging Operations
• Blend Moves
• Preset Operations
• Reset Errors

Diagnostic Mode
Use the configuration mode to select the diagnostic mode of operation. Once selected,
the diagnostic mode allows you to test your program and wiring by connecting the loop back wires at the
translator. The purpose of loop back diagnostics is to test the system wiring for electrical noise.
The number of pulses received at the feedback should equal the commanded number of pulses at the end of the move.
If they are not equal, the system may be experiencing problems due to electrical noise.
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|


Please do not listen to the advice of non-professional engineers! Cause equipment damage!


wechat/whatsapp:
Email: kongjiangauto@163.com
-
Vibro-meter vmf-RLC16-V111 200-570-101-015 200-570-000-111 Relay Card
-
Vibro-meter vmf-IOC4T 200560-101-017 200-560-000-111 I/O module
-
vmf cpum vmf-cmc16 200-530-111-013 200-530-100-014 Vibro-meter Monitoring system Modulee
-
Vibro-meter 200-595-045-114 | CPUM | Vibration Processor Module
-
Vibro-meter SIM-275A 200-582-500-013 state-of-the-art protection and monitoring module
Copyright © 2009 - 2024 Cld , All Rights Reserved K-JIANG All rights reserved