A-B 1747-DCN Introduction Distributed I/O Scanner
DIO System Overview
The DIO system consists of an SLC processor, a scanner, an Isolated Coupler
and I/O blocks. These devices form the DIO System when they are properly
connected to the DIO Link and the DH–485 Data Link as shown below. The
DIO Link and the DH–485 Data Link are independent networks.
The DIO Link consists of the scanner and I/O blocks. It enables the SLC
processor to exchange input and output information with up to 30 I/O blocks.
Output data is transferred from the SLC processor to the scanner, which then
transmits the data to the appropriate I/O block via the DIO Link. The
scanner receives input data from the I/O blocks via the DIO Link. The
scanner then provides this data to the SLC processor. The maximum length
of the DIO Link is 2,500 feet (762 meters) using Belden 9463 cable.
The SLC processor and programming devices communicate using the
DH–485 Data Link. The DH–485 port located on each I/O block allows
remote programming and/or monitoring of the SLC processor. It does not
directly control the I/O block.
Connecting a programming device to any I/O block programming port allows
the programming device to communicate with the SLC processor. The
maximum length of the DH–485 Data Link is 4,000 feet (1,219 meters) using
Belden 9842 cable.
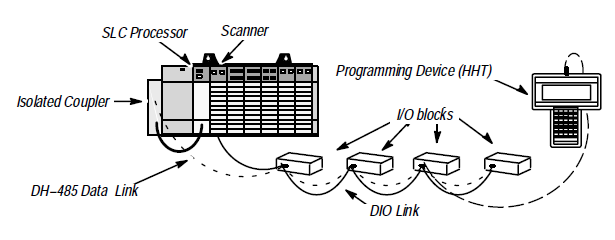
DIO Link Overview
The DIO Link is an Allen–Bradley communications network supporting high
speed transfer of control information. A DIO Link consists of a single
master device (the scanner) and multiple slave devices (the I/O blocks). The
scanner and I/O blocks are daisy chained together by a single twisted pair
cable (Belden 9463).
Each I/O block is assigned a I/O block number from 1 to 31 (excluding 16,
which is invalid) by setting the appropriate dip switches on the I/O block.
I/O block numbers must be assigned consecutively. For example, if 5 I/O
blocks are used, they must be assigned I/O block numbers 1 to 5. I/O blocks
do not have to be wired in a contiguous order. For example, I/O block 5 can
follow I/O block 2.
The inputs and outputs for each I/O block are mapped into the words in the
SLC processor’s input and output images. These words correspond to the
scanner’s slot number and the I/O block’s number. For example, if the
scanner is installed in slot 2 of the SLC Rack, I/O block number 1 will have:
• its input data reflected in word 1 of the slot 2 input image
• its output data reflected in word 1 of the slot 2 output image.
The scanner communicates with each I/O block in a round robin fashion.
The scanner initiates communications with an I/O block by first sending its
output data. The I/O block then responds by sending its input data back to
the scanner. After the scanner completes its I/O transfer with the last I/O
block, it begins another transfer with the first I/O block.
DH–485 Data Link Overview
The DH–485 Data Link is an Allen–Bradley communications network that
supports the transfer of information between programming devices and SLC
processors. The programming device and SLC processor are attached to the
DH–485 Data Link using either an Isolated Coupler or an I/O block. The
DH–485 Data Link may consist of multiple Isolated Couplers and/or I/O
blocks that provide for communication between several programming
devices and/or processors.
The Isolated Couplers and I/O blocks are daisy chained together by a single
twisted pair cable (Belden 9842) to form the DH–485 Data Link. The
programming devices and SLC processors are attached to the Isolated
Coupler or I/O block using Communication Cables (Catalog Numbers
1747–C10 and –C11).
For additional information on the DH–485 Data Link, see the Installation and
Operation Manual for SLC 500 Modular Hardware Style Programmable
Controllers, Publication 1747–804.

- Informations
- Industry information
- ABB
- A-B
- GE
- MOOG
- NI
- YOKOGAWA
- FOXBORO
- BENTLY
- B&R
- UNIOP
- Abaco
- KONGSBERG
- Triconex
- HITACHI
- Emerson
- Honeywell
- Motorola
- Omron
- CTI
- Woodward
- Eaton
- EPRO
- KOLLMORGEN
- SST
- Scanlab
- Reliance
- DFI
- Prosoft
- Rexroth
- Vibro-Meter
- Mitsubishi Power
- Parker
- GEA
- MAN
- ALSTOM
- SBS
- PCH Engineering
- ZYGO
- HIMA
- BIFFI
- Advantest
- KUKA
- Full-V
- DEIF
- IBA
- Euresys
- Vishay
- Meggitt
- Aerotech
- Merlin Embedded
- Baker Hughes
- Horner
- Control Wave
- Schneider
- Siemens
- KEBA
- TEWS
- MERSEN
- Panasonic
- Ingersoll Rand
- Watlow
- Johnson Controls
- irtec
- Baldor
-
Kongsberg TRX32 FILTER (303067B) | Elektro Marine
-
Kongsberg MRU-M-MB3 | Motion Reference Unit
-
Kongsberg TRX32 303088 | eight-channel I/O module
-
Kongsberg MRU2 Motion Reference Unit
-
KONGSBERG MRU-M-SU1 Industrial Measurement Unit
-
Kongsberg RMP201-8 Versatile Remote Input/output System
-
Kongsberg dPSC 8100183 Dual Process Segment Controller
-
YOKOGAWA YS1700-100/A06/A31 Programmable indicating controller
-
YOKOGAWA YS1700-100/A06/A31 Programmable Indicating Controller
-
KS9-5*A | Yokogawa | MXL DSC Cabl
-
KS8-5*A | Yokogawa | MXL DSC Cabl
-
KS2-05*A | Yokogawa | MXL DSC Cabl
-
YOKOGAWA PW482-10 S2 Power Supply Module
-
Yokogawa SCP451-11 S1 Processor Module
-
YOKOGAWA SR1030B62 High-Frequency Module
-
Yokogawa CP451-50 S2 Processor Module
-
YOKOGAWA AAI143-H50 Analog I/O Modules
-
YOKOGAWA AMM42 2-Wire Transmitter Input Multiplexer Module
-
SDV144-S63 | Yokogawa | Digital Input Module
-
Yokogawa AIP830-111 Operation Keyboard for Single loop Operation
-
Yokogawa S9361DH00 Control Module / Terminal Board
-
Yokogawa ATK4A-00/S1 KS Cable Interface Adapter
-
YOKOGAWA PW701 Power Supply Module
-
YOKOGAWA Dual-Redundant V-Network Router AVR10D-A22010
-
YOKOGAWA PW441-10 Communication Module
-
YOKOGAWA VI451-10 S2 Communication Module
-
Yokogawa VC401-10 Coupler Modules
-
Yokogawa ALP121 PROFIBUS-DP Communication Module
-
Yokogawa NFAI841-S00/A4S00 Analog Input/Output Module
-
YOKOGAWA AIP591 Transceiver Control Module
-
YOKOGAWA AIP578 Transceiver Control Module
-
YOKOGAWA PW501 Power Supply Unit Brand
-
Yokogawa YNT511D-V42 Bus Repeater Module
-
YOKOGAWA AIP171 Transceiver Control Module
-
YOKOGAWA VI702 Vnet/IP Interface Card
-
2302-32-VLE-2 YOKOGAWA Data Acquisition Module
-
Yokogawa ATK4A-00 16-Channel KS Cable Interface Adapter
-
YOKOGAWA ALR121-S00 Serial Communication Module
-
CP461-50 | Yokogawa | Processor Module
-
Yokogawa AIP121-S00 Control Module
-
YOKOGAWA UR1800 Wireless Communication Module
-
Yokogawa| LC82 *A Redundant RL-Bus Interface Card
-
YOKOGAWA ST6 Industrial Control Module
-
YOKOGAWA ANR10D ER Bus Node Unit
-
YOKOGAWA SDV144-S13 S1 Digital Input Module
-
YOKOGAWA NFAI143-H00 analog I/O module
-
YOKOGAWA EB501 Bus Interface Module
-
Yokogawa CP451-10-S2 High-Performance Processor Module
-
YOKOGAWA V0/E1/TCAM/L08 High-Precision Temperature Controller
-
YOKOGAWA VO/E2/TCDM24/L8 High-Precision Temperature Controller
-
YOKOGAWA 16137-119 Process Control Module
-
YOKOGAWA 16114-500 I/O Module for Process Control Systems
-
Yokogawa PSCDM024DCBAN - Critical Discrete Module
-
YOKOGAWA 16137-151 Digital Input Module
-
YOKOGAWA 16137-188 Digital Input Module
-
YOKOGAWA 16137-222 Digital Input Module
-
YOKOGAWA 16137-223 Digital Input Module
-
YOKOGAWA 16137-153 Digital Input Module
-
Watlow SUB21/IV10 0-10 V input adaptor
-
Watlow ITOOLS/NONE/USB U SB configuration kit
-
Watlow CTR500000/000 100 A Current transformer
-
Watlow CTR400000/000 50 A Current transformer
-
Watlow CTR200000/000 25 A Current transformer
-
Watlow CTR100000/000 10 A Current transformer
-
Watlow SUB35/ACCESS/249R.1 2.49R Precision resistor
-
Vibro-meter vmf-RLC16-V111 200-570-101-015 200-570-000-111 Relay Card
-
Vibro-meter vmf-IOC4T 200560-101-017 200-560-000-111 I/O module
-
vmf cpum vmf-cmc16 200-530-111-013 200-530-100-014 Vibro-meter Monitoring system Modulee
-
Vibro-meter 200-595-045-114 | CPUM | Vibration Processor Module
-
Vibro-meter SIM-275A 200-582-500-013 state-of-the-art protection and monitoring module
-
Vibro-meter VM600 RLC16 200-570-000-111 200-570-101-015 Relay Card
-
Vibro-meter VM600 RPS6U 200-582-600-013 cutting-edge monitoring module
-
Vibro-meter VM600 CMC16 200-530-025-014 200-530-111-013 input/output card
-
Vibro-meter 200-570-000-014 200-570-101-013 VM600 Protection Module
-
Vibro-meter 620-002-000-113 620-003-111-112 VM600 XIO16T input/output card
-
Vibro-meter 600-003 620-001-001-116 VM600 XMV16 input/output card
-
Vibro-Meter 444-680-000-511 Level Detector & Proximity Sensor
-
Vibro-meter VM600 MPC4 200-510-111-034 200-510-070-113 Module
-
Vibro-Meter IOCN 200-566-000-113 | I/O Communication Node
-
Vibro-meter VM600 IOC16T 200-565-000-013 / 200-565-101-013 Industrial Control Module
-
Vibro-Meter 200-566-000-012 VM600 IOCN Communication board
-
Vibro-meter 200-560-000-113 VM600 power supplies Module
-
VIBRO 573-935-202C - High-Accuracy Interface Module
-
Vibro-meter 200-595-002-011 Modular Safety Relays
-
200-560-000-016 VIBRO I/O Module
-
YOKOGAWA 8662570000 Terminal Module
-
YOKOGAWA 8596020000 Terminal Module
-
YOKOGAWA 8662560000 Terminal Module
-
YOKOGAWA PSCAMAAN | Process Control Analog Input Module
-
YOKOGAWA DR1030B60 High-Precision Pressure Transmitter
-
Yokogawa adv551 Digital I/O Modules
-
Yokogawa aai543 Analog I/O Modules (for FIO)
-
YOKOGAWA LR 4220E Level Controller Module
-
Yokogawa SR1008B62 Signal Relay Module
-
SC200S | Yokogawa Electric Corporation
-
Yokogawa PW301 Power Supply
-
YOKOGAWA NP53*C - Precision Control Module
-
Yokogawa F3YD64-1A Basic Input/Output Modules
-
Yokogawa F3XD64-3N Basic Input/Output Modules
-
Yokogawa F3WD64-3N Input/Output Module
-
Yokogawa F3SP21-0N CPU Module
-
YOKOGAWA F3PU10-0N Power Supply Module
-
YOKOGAWA F3PU06-0N Power Supply Module
-
YOKOGAWA F3NC02-0N Positioning Module
-
YOKOGAWA F3NC01-0N Positioning Module
-
YOKOGAWA PLC F3LC21-1N MULTI-LINK MODULE
-
YOKOGAWA F3BU06-0N Base Module
-
Honeywell DC-TFB412 51307618-176 Control Module
-
Honeywell DC-TCF901 51307593-176 9-Port Control Firewall Module
-
Honeywell DC-TCF901 cutting-edge control module
-
Honeywell DC-TFB412 Circuit Board
-
LVCDJW00000750A Watlow (Temperature Limit Controller)
-
Watlow 84700-0003 Dust cover
-
Watlow 847290006 USB type A panel mount with 2 m cord
-
Watlow RJF 21N SCC RJ45 receptacle with self closing cap
-
Watlow USBBF 21N SCC USB - B receptacle with self closing cap
-
Watlow USBF 21N SCC USB - A receptacle with self closing cap
-
Watlow 0600-0097-0000 Mixed I/O Flex Modules Quick Start Guide
-
Watlow 0600-0096-0000 High Density Flex Modules Quick Start Guide
-
Watlow 0600-0095-0000 Communications Flex Modules Quick Start Guide
-
Watlow 0600-0094-0000 F4T Controller Quick Start Guide
-
Watlow 0600-0093-0000 Setup and Operations User Guide
-
Watlow 0600-0092-0000 Installation and Troubleshooting User Guide
-
Watlow 0822-0769-0000 Module slot plug (for vacant F4T slots without flex modules
-
Watlow 0830-0858-0000 Replacement battery
-
Watlow 0830-0808-0002 (CAPUSB-A) Rubber plug USB host
-
Watlow 0830-0808-0001 (CAPUSB-MB5) Rubber plug USB mini
-
Watlow 0601-0001-0000 Controller support tools (DVD)


wechat/whatsapp:
Email: kongjiangauto@163.com
-
Vibro-meter vmf-RLC16-V111 200-570-101-015 200-570-000-111 Relay Card
-
Vibro-meter vmf-IOC4T 200560-101-017 200-560-000-111 I/O module
-
vmf cpum vmf-cmc16 200-530-111-013 200-530-100-014 Vibro-meter Monitoring system Modulee
-
Vibro-meter 200-595-045-114 | CPUM | Vibration Processor Module
-
Vibro-meter SIM-275A 200-582-500-013 state-of-the-art protection and monitoring module
Copyright © 2009 - 2024 Cld , All Rights Reserved K-JIANG All rights reserved
